How to design the laboratory ventilation system?
Category : Blog
Laboratory ventilation is critical to maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. A well-designed laboratory ventilation system removes hazardous chemicals, fumes, and particulates to provide a safe working environment for laboratory personnel. Additionally, a well-designed ventilation system can prevent the build-up of air pollutants at dangerous levels, thereby preventing explosions, fires, and other safety hazards.

Designing a laboratory ventilation system requires careful consideration of several factors, including the types of chemicals and processes used in the laboratory, the size and layout of the laboratory, and the number of people working in the laboratory.
Key Factors to Consider When Designing a Laboratory Ventilation System
The first step in designing a laboratory ventilation system is to identify the sources of air pollutants in the laboratory. This can include chemicals, solvents, gases and particulates. Once the sources have been identified, the next step is to determine the appropriate ventilation rate for each source. This can be calculated using a variety of factors, including the quantity and volatility of the substance, the size of the laboratory, and the number of people working in the laboratory.
Once the ventilation rate has been determined, the next step is to design the ventilation system. The ventilation system must be able to provide the required ventilation rates to all areas of the laboratory. This may involve the use of ventilation ductwork, laboratory fume hoods, variable air volume dampers, blowers, and other components to maintain the air in the laboratory.
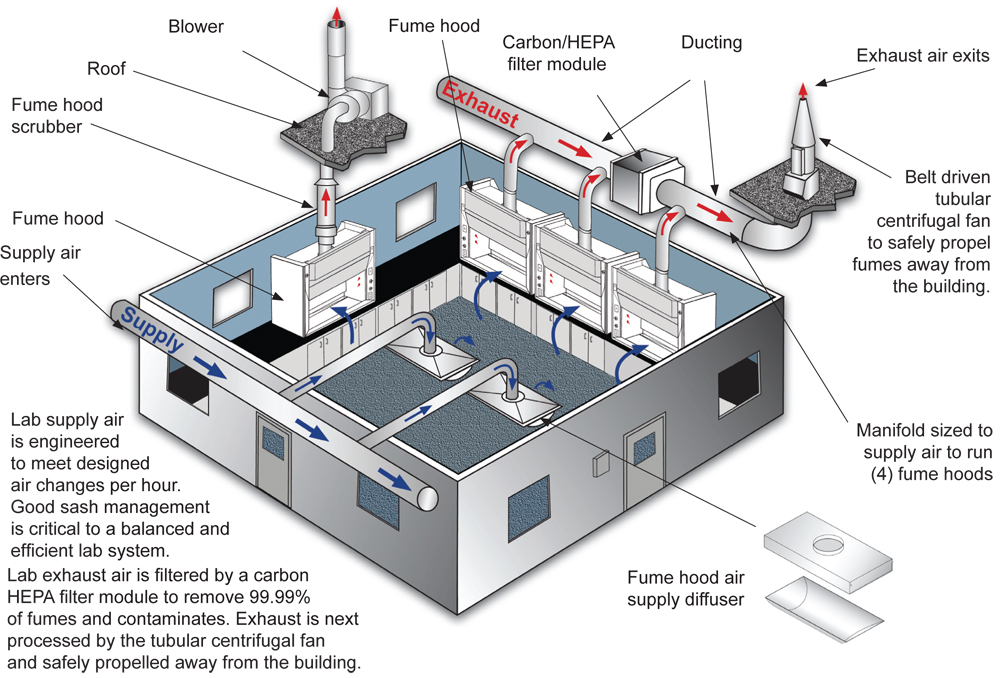
When designing a ventilation system, it is important to consider the location of the intake and exhaust openings. The air intake should be located in an area free of contamination, such as the roof of a building or in an area away from potential sources of contamination. The exhaust should be located in an area that allows the safe removal of contaminated air, such as the roof of a building or in an area away from other air intakes.
In addition to the design of the ventilation system, it is important to consider the maintenance and testing of the system. Ventilation systems should be inspected and tested regularly to ensure they are functioning properly and providing the required ventilation rates. This may involve the use of airflow meters, smoke tests and other tools to verify the effectiveness of the ventilation system.

It is also important to consider the type of filter used in the ventilation system. Filters should be able to remove specific contaminants found in the laboratory. Additionally, filters should be replaced regularly to maintain the effectiveness of the ventilation system.
Another important factor to consider when designing a laboratory ventilation system is the use of local exhaust ventilation fume hoods. The laboratory fume hood can quickly absorb the harmful gases produced in the laboratory process, and can best ensure the personal safety of the experimenters. This is especially effective where there are high concentrations of pollutants, such as during chemical reactions or when handling hazardous materials.
Finally, it is important to consider the training of laboratory personnel. Laboratory personnel should be trained in the proper use of the ventilation system, including how to operate the system and how to recognize potential problems with the system. The operation process can be simplified by adding an automatic control system.
In summary, designing a laboratory ventilation system requires careful consideration of a variety of factors, including sources of contaminants, required ventilation rates, location of intake and exhaust outlets, and maintenance and testing of the system. By following these guidelines, laboratory personnel can ensure that their ventilation systems provide a safe and healthy work environment.